
Second Class Lever Examples NelsonabbRamsey
There are three different kinds of levers: first class, second class, and third class. Each of these lever classes have unique arrangements of the muscle's insertion (effort) and bones (lever/arm) around the joint (fulcrum). See the chart below to visualize the difference between the levers: Effort Arm vs. Load Arm
The mechanics in biomechanics online presentation
The most common and popular lever can be found in many playgrounds: a see-saw or teeter-totter. They are found everywhere and it is one of the most useful simple machines. There are three classes of levers. The image below is an example of a Class Two Lever, sometimes called a Second Class Lever.

State the characteristics of class II lever and give two examples.
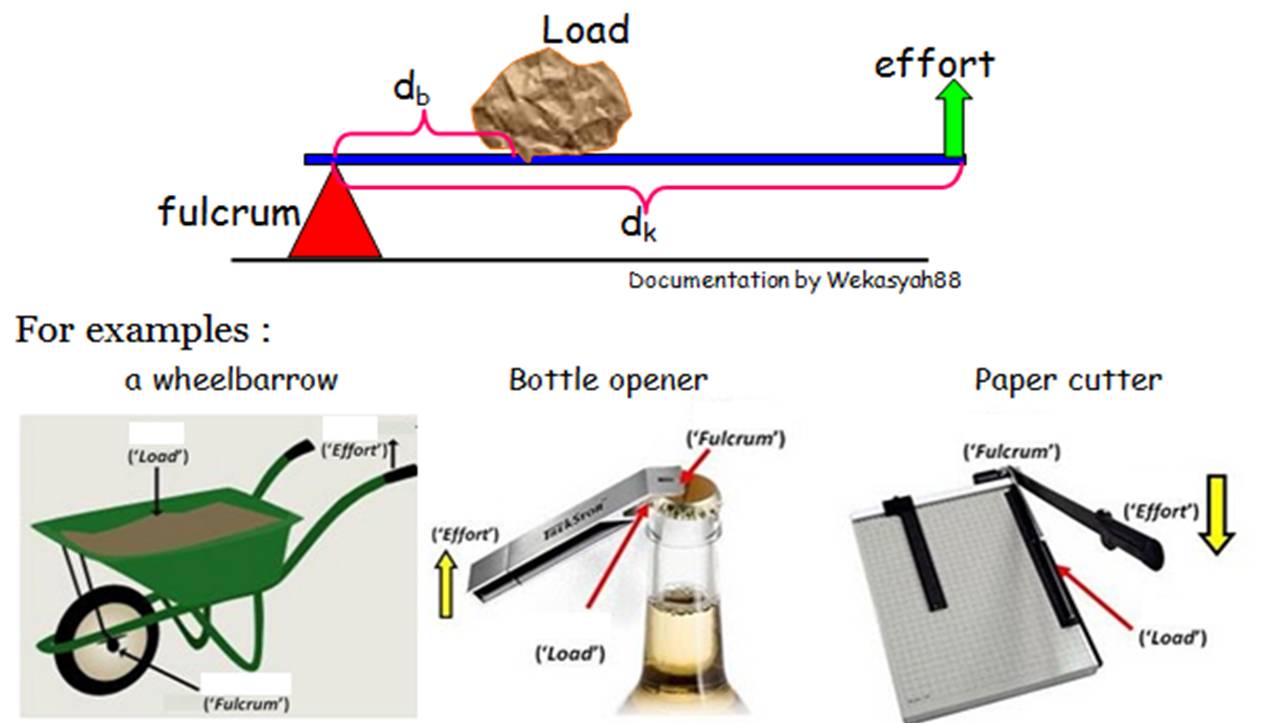
A wheelbarrow, a bottle opener, and an oar are examples of second class levers. Second class levers are used in wheelbarrows (left), when going on tiptoes (centre) and when doing push-ups (Sources: MarkusHagenlocher [CC BY-SA 3.0] via Wikimedia Commons , BruceBlaus [CC BY-SA 4.0] via Wikimedia Commons and U.S. Navy [Public domain] via Wikimedia.
Simple Machines Levers Let's Talk Science
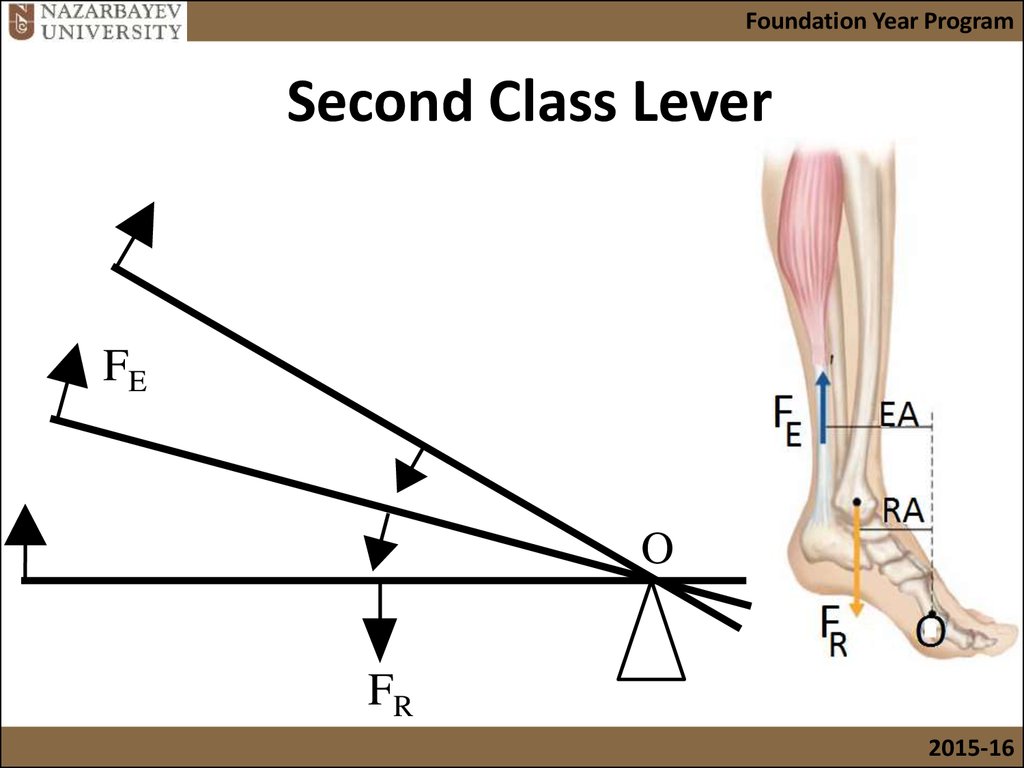
A lever is a rigid object used to make it easier to move a large load a short distance or a small load a large distance. There are three classes of levers, and all three classes are present in the body [1][2]. For example, the forearm is a 3rd class lever because the biceps pulls on the forearm between the joint (fulcrum) and the ball (load).
PPT Lever Systems PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID174578
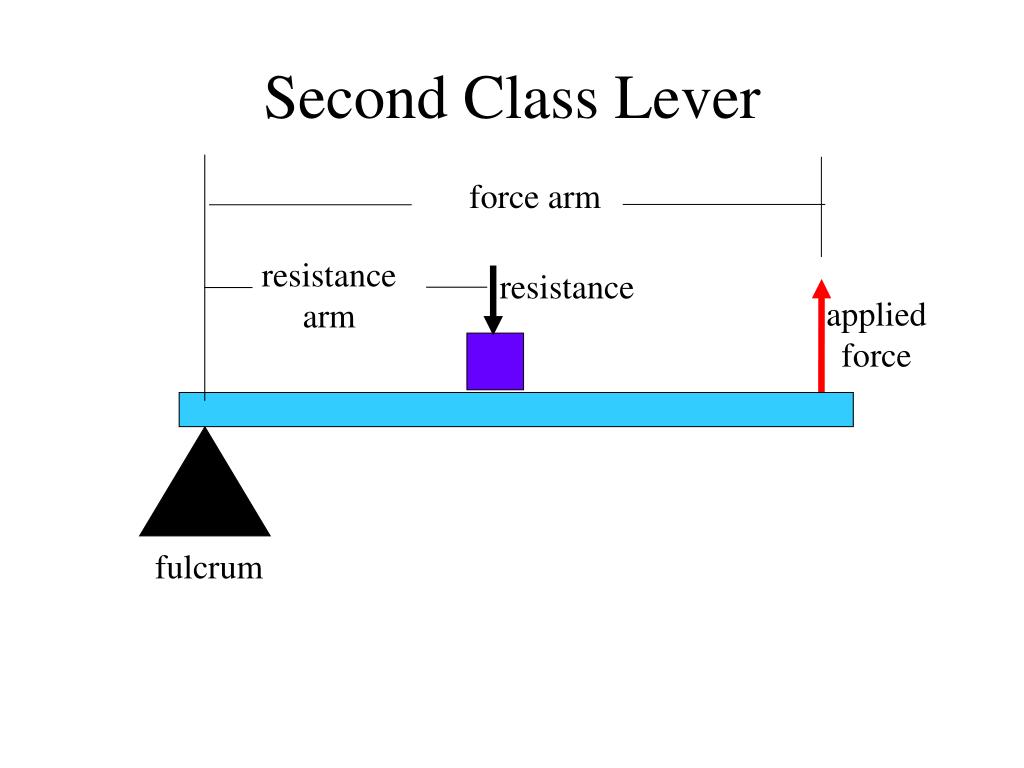
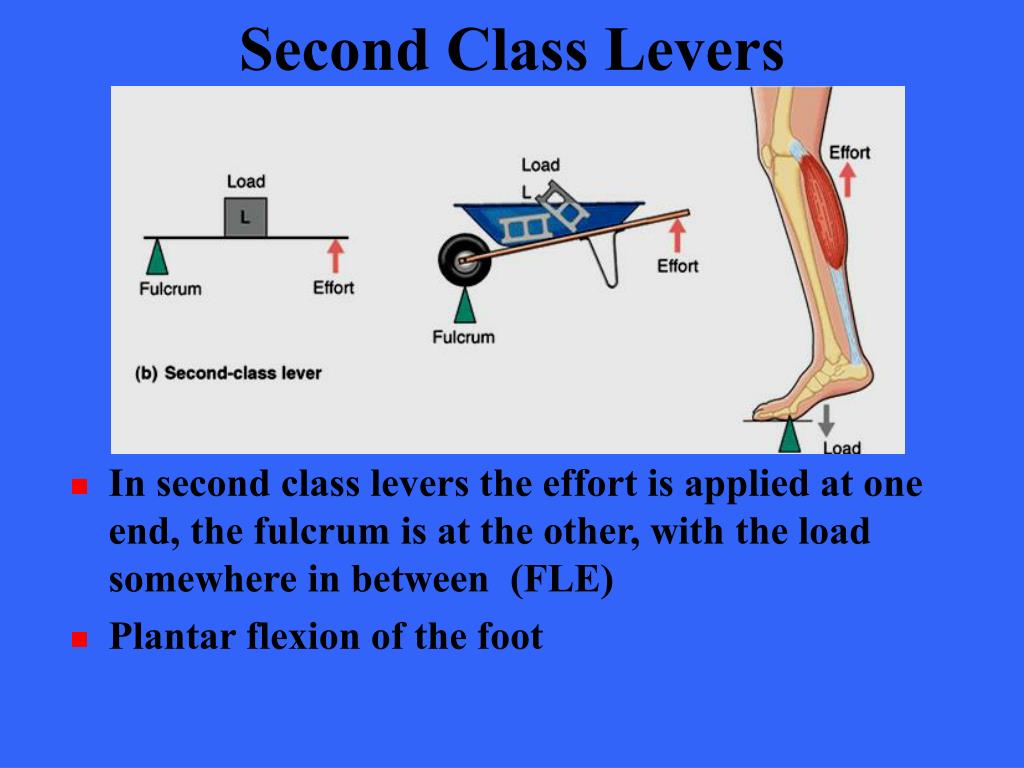
Quick Reference. A lever that has its point of resistance (load) between its fulcrum (point of support or axis of rotation) and point of effort (force application). In the human body, a second class lever is used when a person stands on tip-toe. second-class lever. From: second-class lever in The Oxford Dictionary of Sports Science & Medicine.
Science online The types of the levers and the importance of each of them
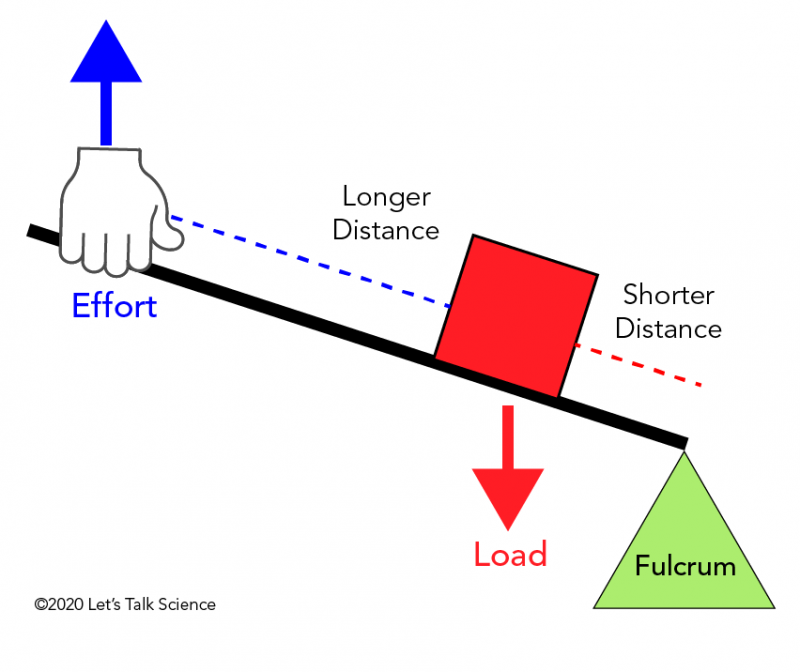
In second class levers the load is between the effort (force) and the fulcrum. A common example is a wheelbarrow where the effort moves a large distance to lift a heavy load, with the axle and wheel as the fulcrum. In a second class lever the effort moves over a large distance to raise the load a small distance.

PPT Simple Machines Discussion PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1897167
Principle of a lever. If you want to move a very large load with a small applied force, it is necessary to put the fulcrum very close to the load. What is different about 2nd class levers. 2nd class levers are interesting, as the fulcrum is at one end, the applied force at the other, and the load that is to be moved is between them.

2nd Class Lever Video YouTube
Second class levers always have the load closer to the fulcrum than the effort, so they will always allow a smaller effort to move a larger load, giving a mechanical advantage greater than one. First class levers can either provide mechanical advantage or increase range of motion , depending on if the effort arm or load arm is longer, so they.

SKI LEVERS The Skier's Manifesto
A wheel and an axle. Pulling a nail out of a wooden plank. In a first-class lever, the force if found to move over a larger distance in order to move the load a smaller distance and the fulcrum is found within the force and the load. 2. Second-Class Lever: ( Types of Lever ) Second Class Lever.

Types of Lever Class 5 CBSE Class Notes Online Classnotes123
In second class levers the load is between the effort (force) and the fulcrum. A common example is a wheelbarrow where the effort moves a large distance to lift a heavy load, with the axle and wheel as the fulcrum. In a second class lever the effort moves over a large distance to raise the load a small distance. Table of Contents show.

The 3 Classes of Levers
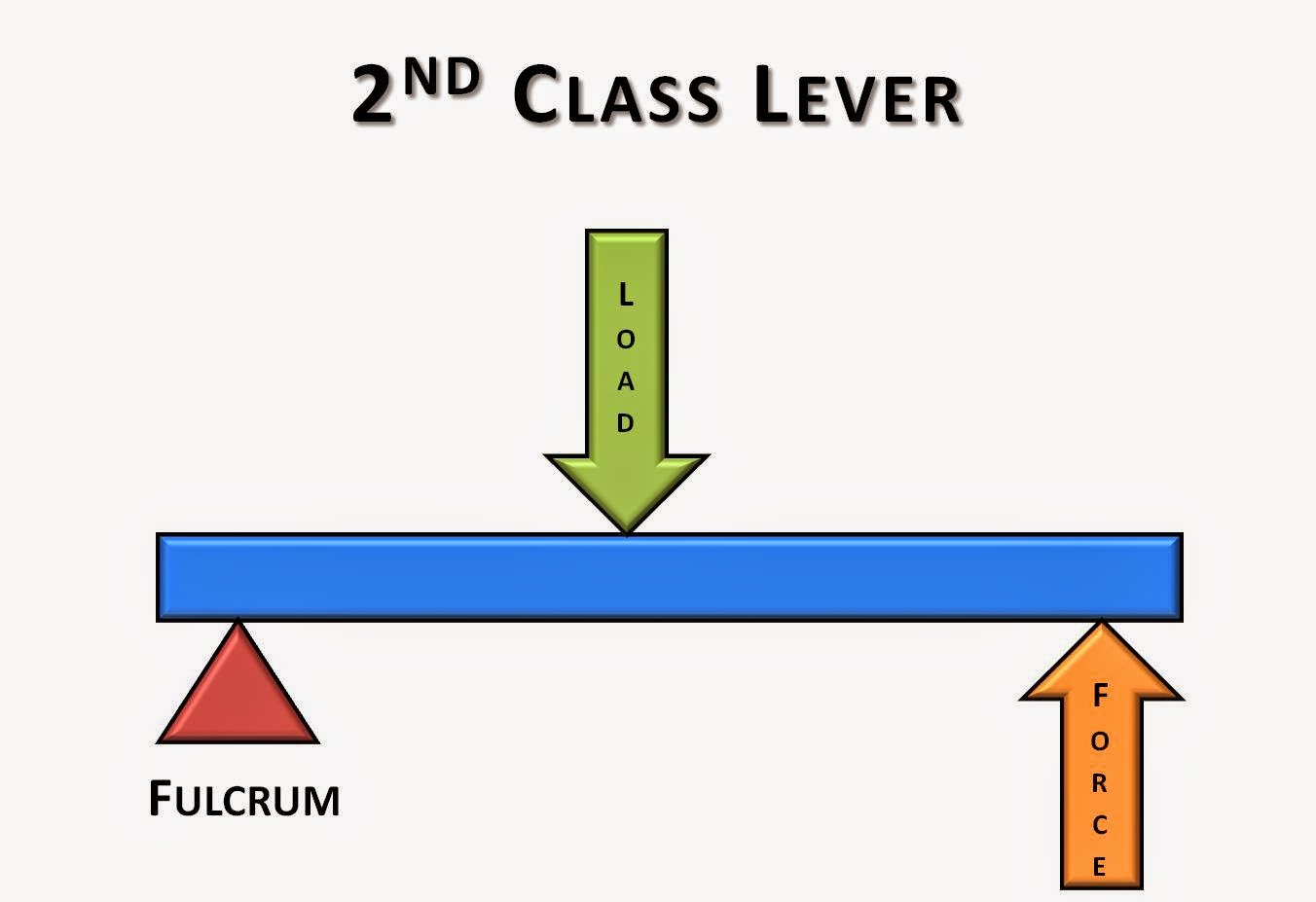
A level where the load and effort force are located on the same side of the fulcrum is often characterized as a second-class level mechanism. Example - Second-Class (Order) Lever. A force (weight) of 1 pound is exerted at a distance of 1 ft from the fulcrum. The effort force at a distance of 2 ft from the fulcrum can be calculated as. F e = (1.

PPT Simple Machines & Their Mechanical Advantages PowerPoint Presentation ID6098995
yes in the 2nd class lever the load is near the fulcrum eg luggage bag. ( 2 votes) Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere.
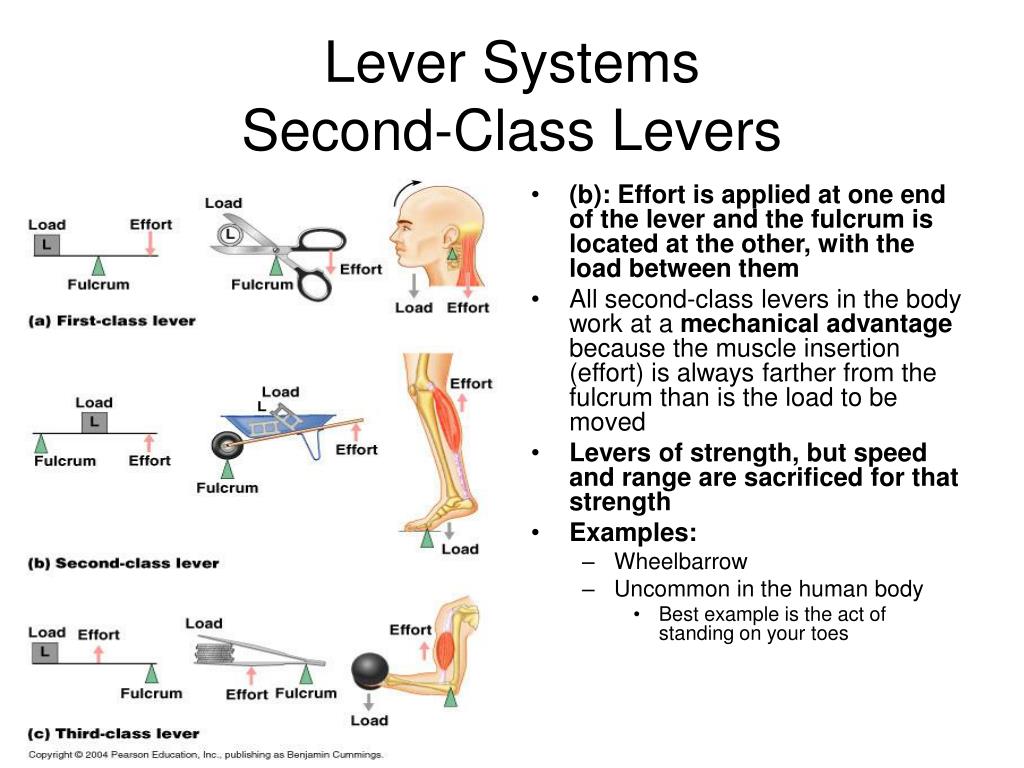
PPT THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1184642
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or fulcrum.A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, load and effort, the lever is divided into three types.It is one of the six simple machines identified by Renaissance scientists. A lever amplifies an input force to provide a greater.
PPT Muscles of the Body PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6195457
The three types of levers are as follows: (1) First Class lever or class I lever, (2) Second Class lever or class II lever, and. (3) Third Class lever or class III lever. These types are based on the relative position of the fulcrum, load, and effort in the lever body.
Pictures Of Second Class Levers Most Expensive Dildo
Second-class levers are also relatively uncommon in the body. One example is raising yourself up on your toes. The pivot is based at the front of the foot, the load is the weight of the body, and the force is applied through the Achilles tendon in the heel. All second-class levers in the body act at a mechanical advantage since the force is.

The 3 Classes of Levers
Anatomy of Levers, Part 3: Second-Class Levers. The second-class lever is another example of a simple machine comprising a beam placed upon a fulcrum. In the second-class lever, the orientation and distribution of forces are different than in the first-class lever: The load is placed between the fulcrum and effort, while the force of the effort.